Rehabilitation
Feasibility of the use of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the rehabilitation of the cancer and neurological patients.
Rehabilitation (Late Latin rehabilitatio meaning restoration) is a system of medical, training and health-promoting measures aimed to prevent and treat pathological conditions that can lead to the temporary or persistent disability. Rehabilitation is meant to restore the ability to live and work under common conditions after the injury or disease as soon as possible. Understanding of the idea of rehabilitation is closely associated with the understanding of terms of “health” and “disease”. There should be a clear definition of the primary signs of health disorders to start restoration of the health. Controversy in understanding of such fundamental notions leads to contradictions and coinage of terms like “medical rehabilitation”, “complex rehabilitation”, “reparative treatment”, “reparative medicine” and other. Rehabilitation is the set of medical, psychological, training, pedagogic and other measures aiming at maximum restoration or compensation of the disordered or damaged psychic and physiological functions and needs of the human body and its working capacity. 
The basic needs of a human include health and healthy progeny, high physical activity, freedom of movement, independence of actions, ability to perform the activities of daily living and to assist others in them, communication with other people, ability to find, receive and use information, self realization through working activity and other types of activities. As distinct from therapy, rehabilitation is administered in absence of acute phase of the disease. Rehabilitation implies medical and pedagogical correction of movement, speech and psyche in older children and adults.
There are several pathological factors that lead to patient’s disability and raise question about the necessity of rehabilitation. In infants they include various prenatal disorders of the nervous system, birth injuries of the brain. In older children the disabling injuries of nervous system may include the injuries of the brain and spinal cord, infectious and inflammatory diseases, for example, consequences of meningitis, encephalitis, poliomyelitis, arachnoiditis, the degenerative diseases of nervous and muscle systems. In adults the most frequent causes of the disability are the injuries and vascular diseases involving disorders of cerebral blood supply. At all stages of rehabilitation, the complex treatment is administered aiming to restore the damaged function with physical training, physiotherapy and medicines.
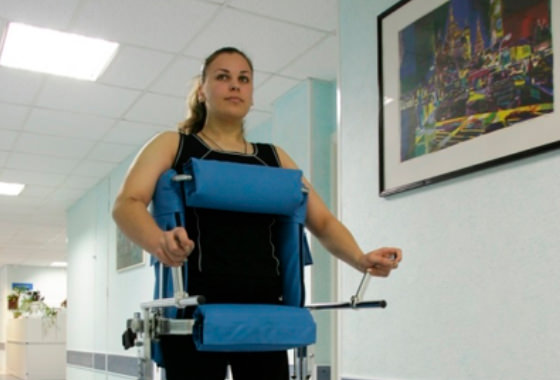
The main stage of rehabilitation is restoration of the cellular, humoral and metabolic homeostasis of the body. This can be achieved with the cell-based preparations. Administration of biomedical cell products, blood components and restoration of the electrolyte and acid-alkaline balance are of key importance in the rehabilitation.
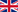
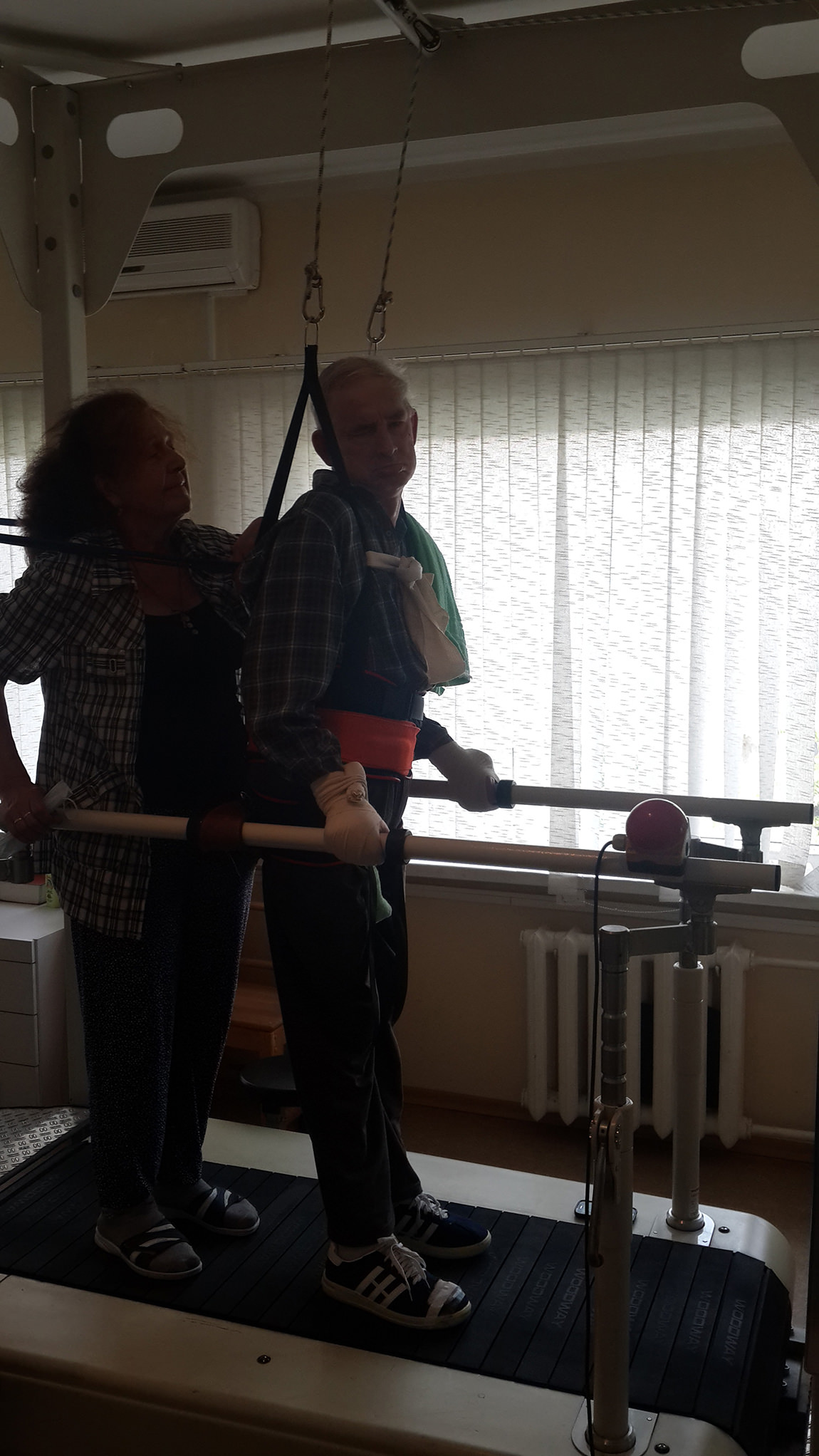 An important element of the complex approach to rehabilitation is use of the hardware resources to facilitate the work and expand the opportunities of the rehabilitation specialists in the physical training and physiotherapy improving the outcome of the treatment and rehabilitation, for example, the equipment assisting in the restoration of walking or arm and hand functions. It is important to pay attention to the pedagogic work and appropriate speech training. The number of the patients who return to work can considerably increase after rehabilitation. It is also important to provide for the succession of the stages of rehabilitation and it should be timely and long-term.
An important element of the complex approach to rehabilitation is use of the hardware resources to facilitate the work and expand the opportunities of the rehabilitation specialists in the physical training and physiotherapy improving the outcome of the treatment and rehabilitation, for example, the equipment assisting in the restoration of walking or arm and hand functions. It is important to pay attention to the pedagogic work and appropriate speech training. The number of the patients who return to work can considerably increase after rehabilitation. It is also important to provide for the succession of the stages of rehabilitation and it should be timely and long-term.